NovaMorphiX LabsYour Partner in Innovation for EU Funding Success
We provide a comprehensive suite of services to empower academia in successfully executing and implementing their EU Funded research projects.
Who We Are
NovaMorphix Labs
EU based network of experts dedicated to helping innovators bring their ideas to life. We specialize in providing the technical and project management services crucial for success in the competitive landscape of EU fund research.
We specialize in transforming early ideas into aesthetical, functional, and manufacturable prototypes—ready for fundraising, production hand-off, or small-batch manufacturing.
The studio uniquely fuses industrial design, mechanical engineering, prototyping (3D printing + CNC), DFAM/DFM consulting, providing end-to-end technical execution with a focus on real-world manufacturability.
Why Choose Us
Solutions You Can Count On
A complete design-to-fabrication workflow - from industrial design through CAD, FEA, and prototyping.
Speed and modularity - structured service bundles allow fast execution
Aesthetic and functional balance - attention to form and CMF (color, material, finish) without compromising on structural integrity or manufacturability. Every prototype comes with production-grade CAD, and material specs.
Visual storytelling - (professional photography, 360° spins, and short-form videos, enhancing grant reports, pitch decks, and product launches.
Competitive pricing via local partner network
Portfolio
Services
Frequently Asked Questions
We work with research teams, startups, and SMEs supporting digitalisation and developing physical products—from early concepts to pilot-ready prototypes. Perfect for Horizon Europe grantees.
We specialize in CAD/CAM/CAE, 3D Printing, AI Integration, Data Analysis and High-Performance Computing, Expert Systems (Knowledge Graphs, LLMs, Probabilistic Programming), project management, communication, dissemination and exploitation activities.
Yes. All services are modular and can be booked individually or as part of a bundle. We also offer consulting and training as standalone options.
Contact
Mission
We are a collective of researchers, innovators, engineers, and project managers passionate about turning ambitious ideas into reality. Our mission is to empower European research teams, startups, and innovation entrepreneurs by providing access to cutting-edge technology, deep industry expertise, and strategic project support, with a special focus on the EU research and innovation ecosystems. We support you through the entire journey to transform your vision into reality - from design, engineering, and prototyping through project management to communication, and exploitation activities.
Vision
To provide an ecosystem where product development becomes modular, intelligent, and accessible—bridging design, grant reporting, and on-demand manufacturing into a unified, AI-supported platform that redefines how physical products are imagined, built, and brought to life.
Values
1. Precision with Purpose: balancing aesthetics, function, and manufacturability at every stage.
2. Human-Centered Technology: AI and automation can empower creativity as a structured, repeatable, and scalable process and emhance human vision, speed, and decision-making.
3. Accessibility: tools and services must reduce barriers—so more people can design, launch, and scale what they believe in.
Services
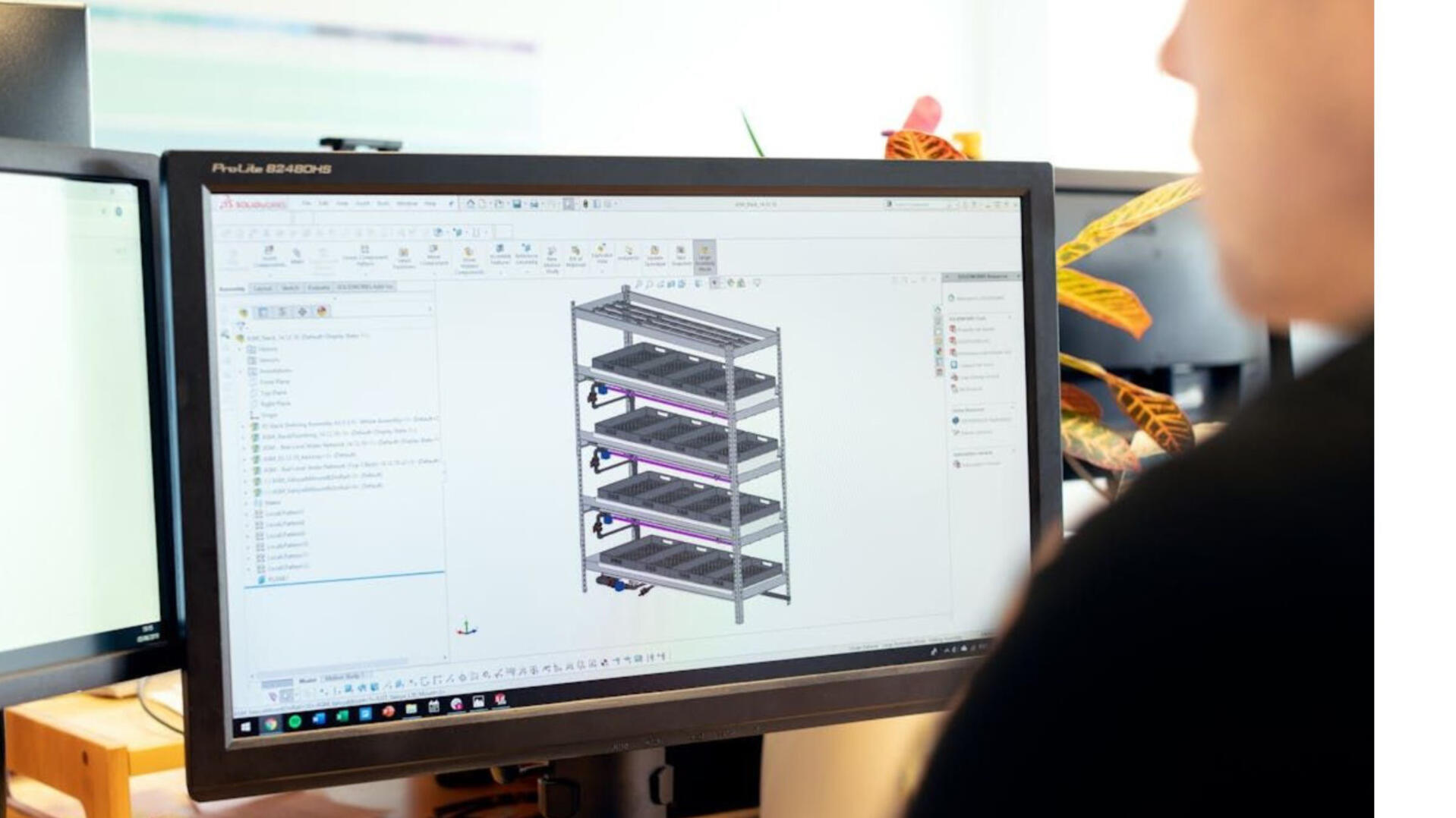

Computer-Aided Design (CAD) & Mechanical Design: 2D drawings, 3D Models, Bill of Materials (BoMs), assemblies, exploded views.
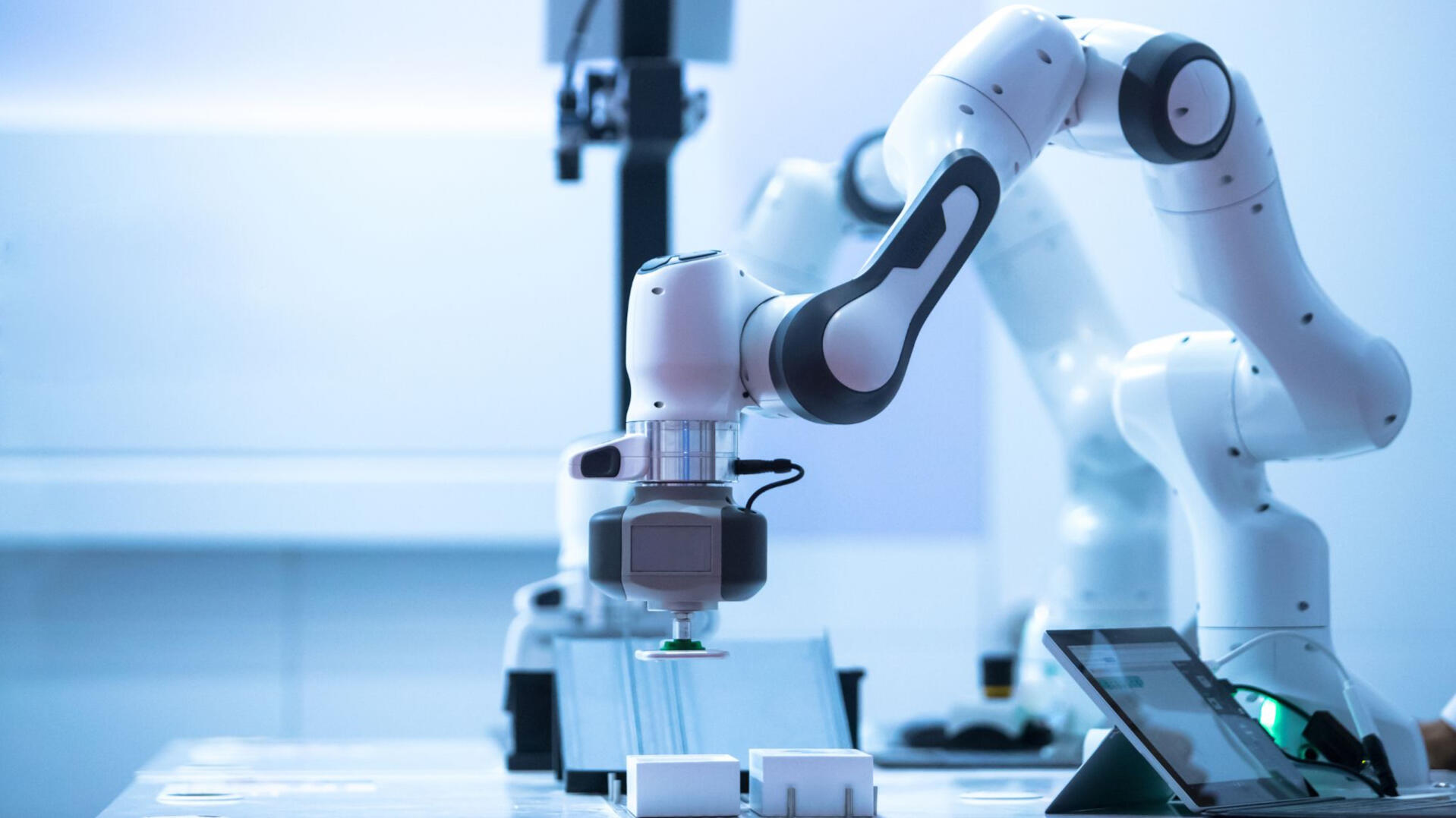

Design for Robotics: End-to-end mechanical design and
prototyping for robotics startups and research teams.
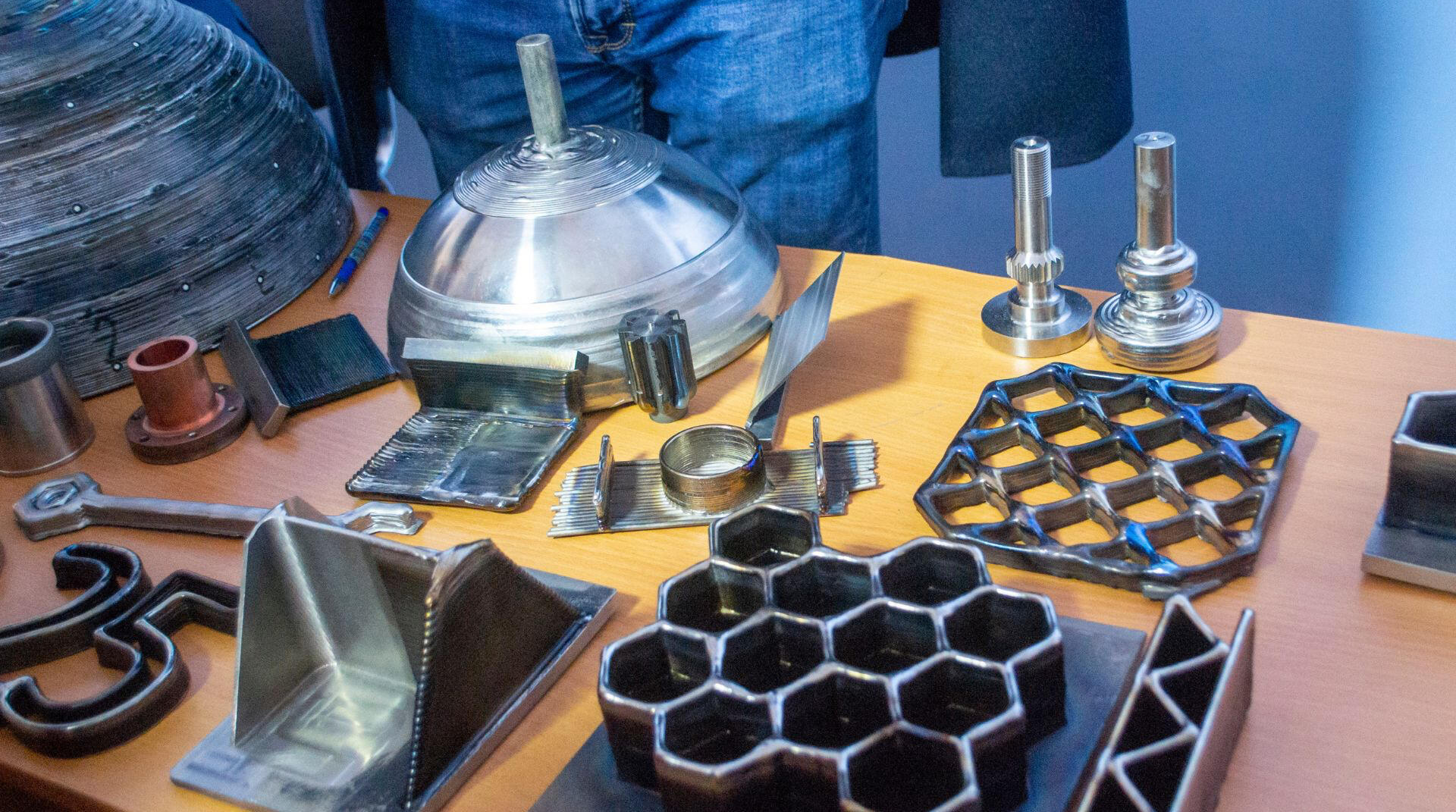

3D Printing: FDM, SLA, SLS (polymers and metals)
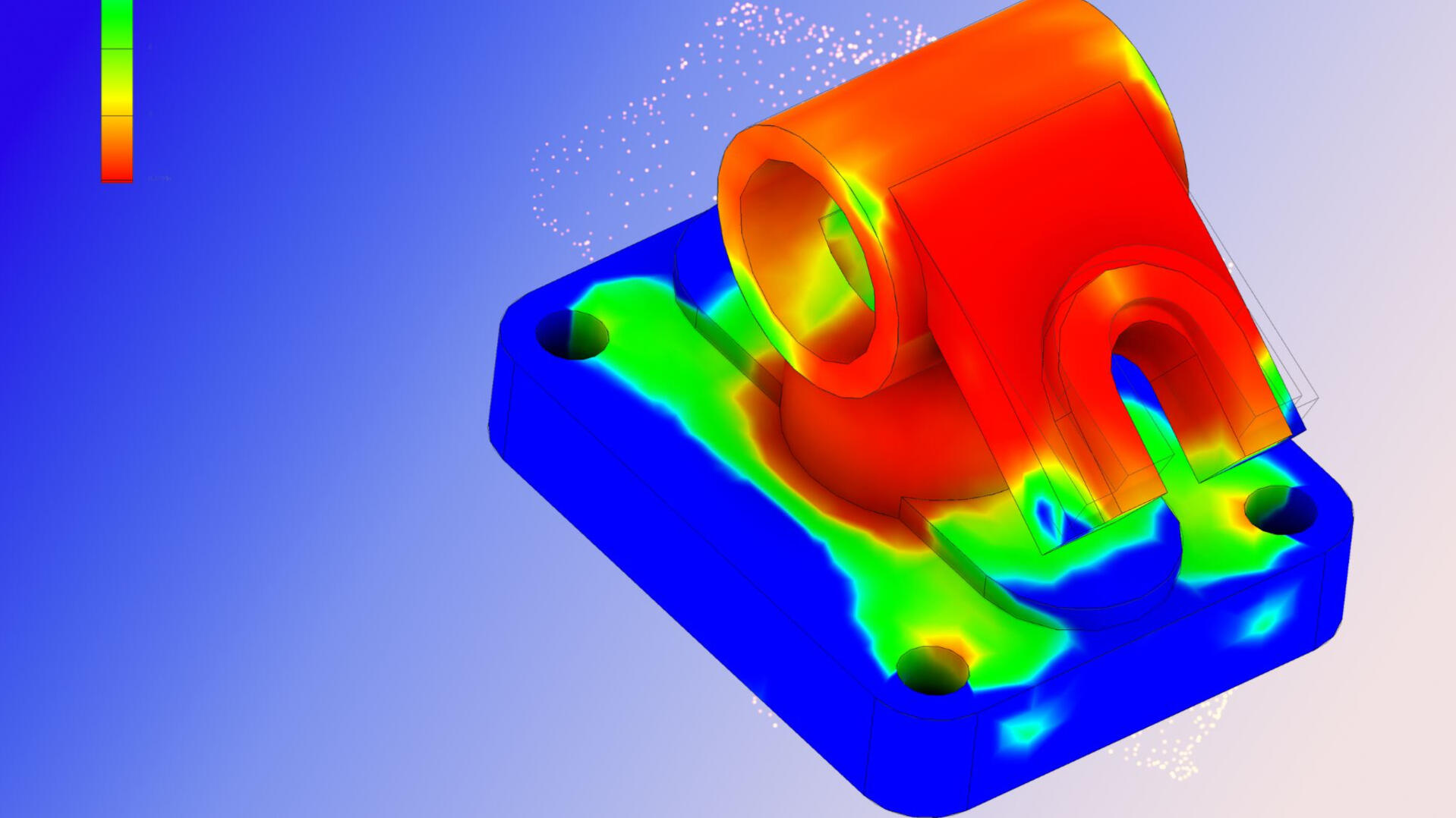
Finite Element Analysis (FEA): stress, thermal
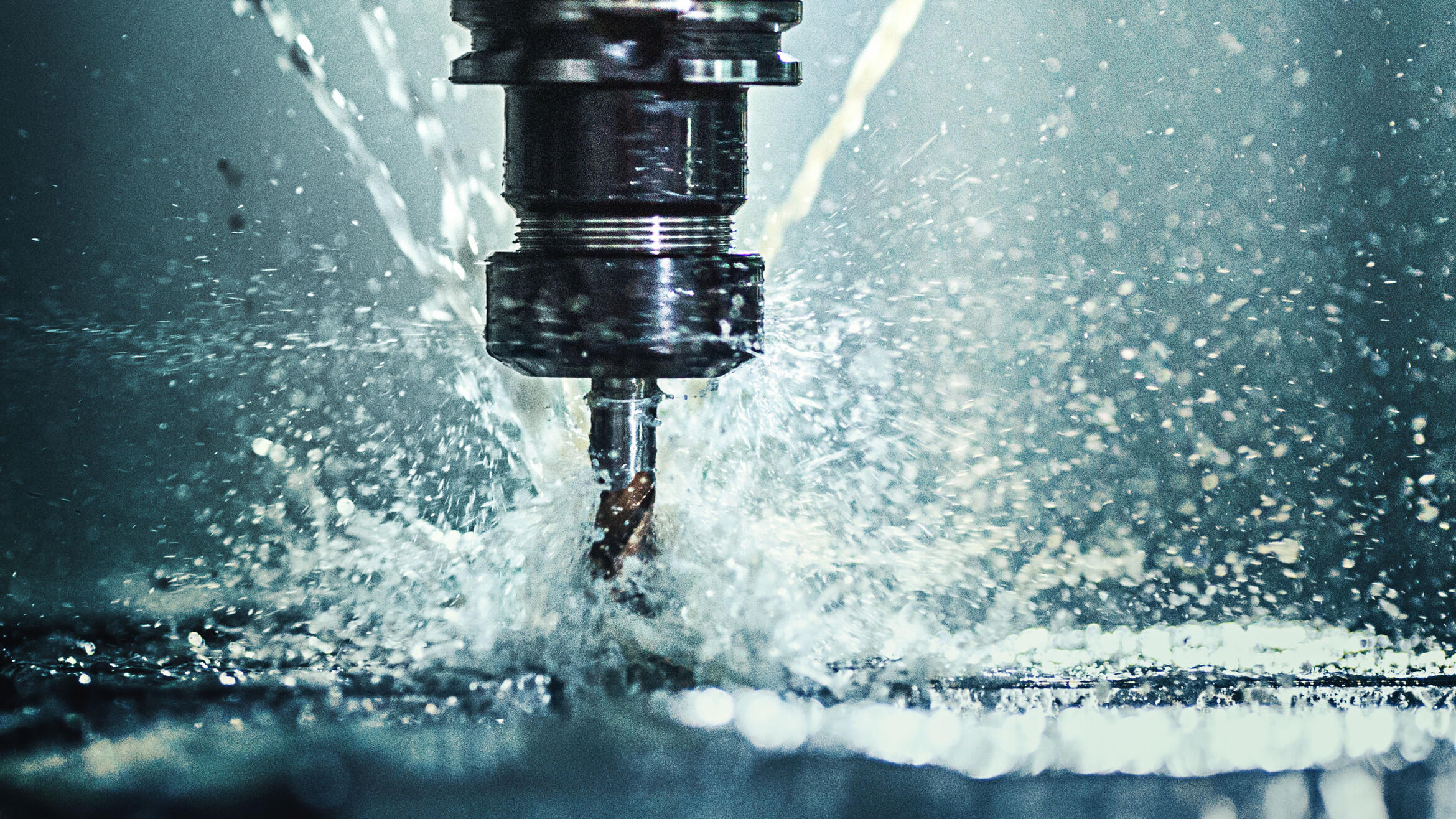

CNC Machining: 3- and 4- axis CNC milling and turning for metals & plastics.
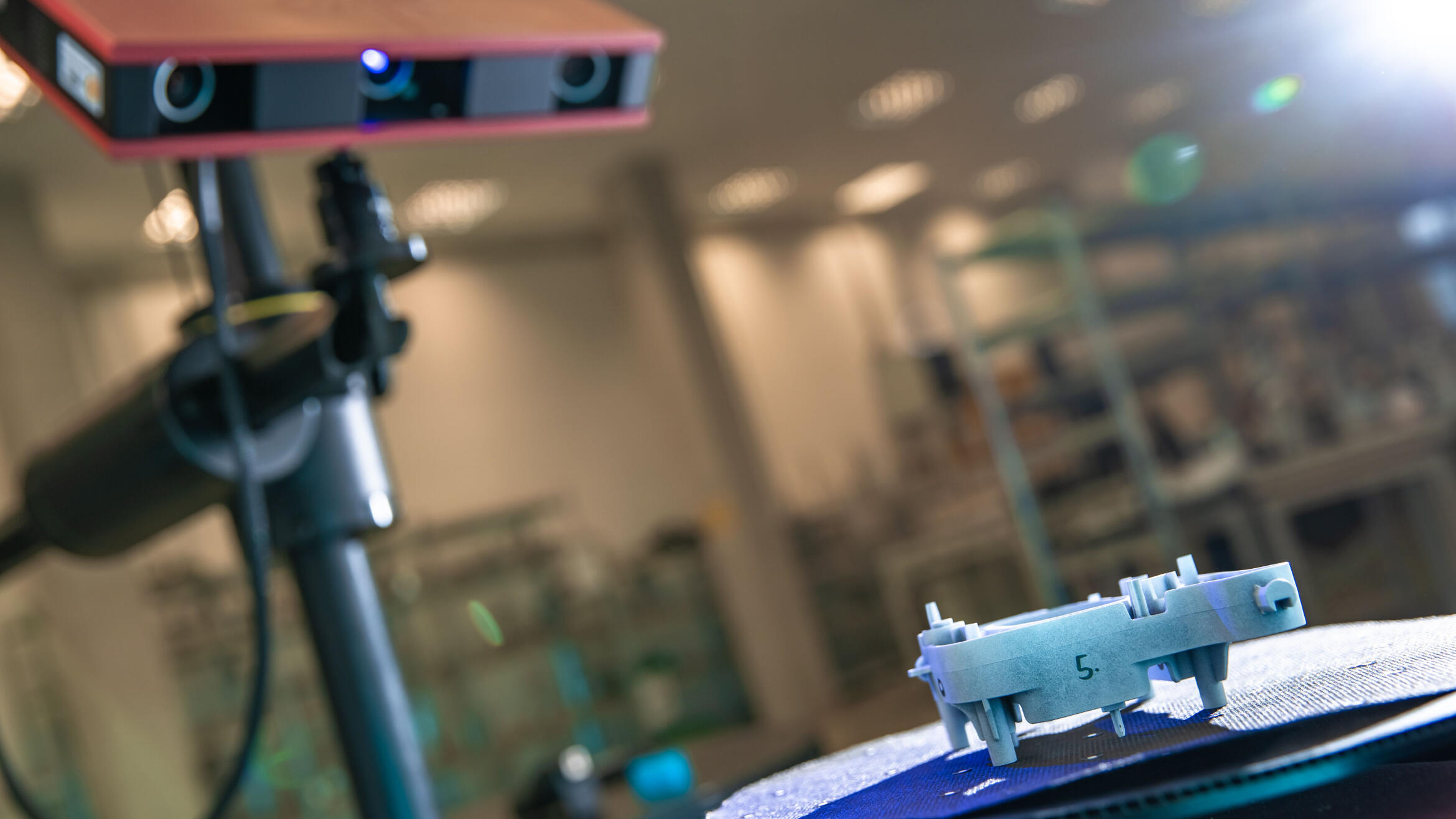

3D Scanning: reverse engineering, inspection

Digital & AI Solutions: AI Integration, High-Performance Computing (HPC) & HPDA, Expert Systems (Knowledge Graphs, LLMs, Probabilistic Programming)Data Analysis

Consulting and supporting services: Project management, EU funding, communication, exploitation and dissemination activities, market validation, professional product photography and videos.
Portfolio
Selected Projects & Designs
Design of a Robot with Open Kinematics Structure, Driven by Shape Memory Alloy Wires
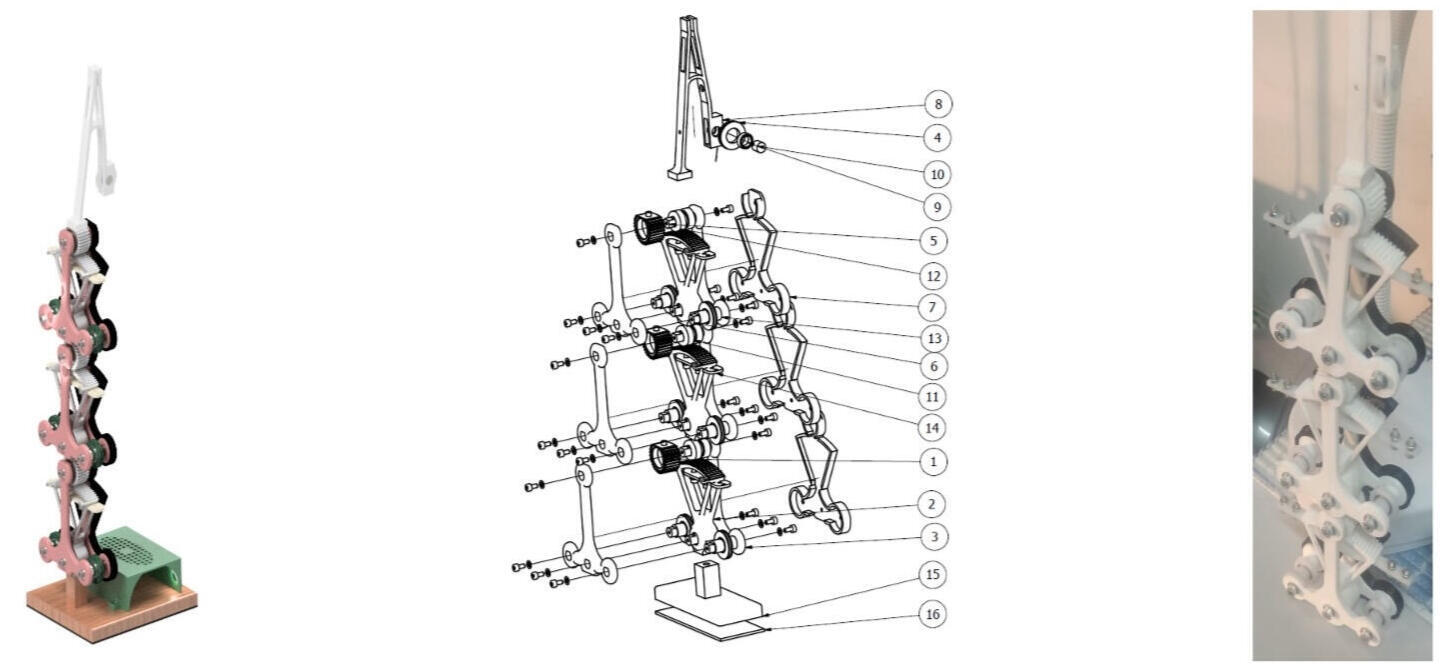
This work presents the design and development of a robotic manipulator with an open kinematic structure, actuated by shape memory alloys (SMAs). The proposed robot features a modular configuration with planetary gear-based links, enabling an expanded working area and enhanced redundancy. The modular approach facilitates adaptability, allowing deployment in various applications, and complex manipulation scenarios.
The research encompasses the complete design process, including kinematic and kineto-static analyses to optimize system performance. A detailed study of SMA wires is conducted to determine their optimal parameters for actuation (maximum force, reaction time, deformation, activation temperature and speed). The work area of the manipulator is analyzed to ensure functional efficiency. Additionally, CAD models and technical drawings of all components are created, followed by a structural strength analysis to validate mechanical integrity.
A prototype of the robot is 3D printed. A basic control system is implemented using a direct current (DC) power supply to regulate the actuation of SMA-driven mechanisms.
Finally, a cost analysis is conducted to evaluate the economic feasibility of the proposed design.
The outcomes of this research contribute to the advancement of modular, SMA-actuated robotic systems with enhanced flexibility and operational capabilities.
Technical Drawings
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
In-Pipe Inspection Robots
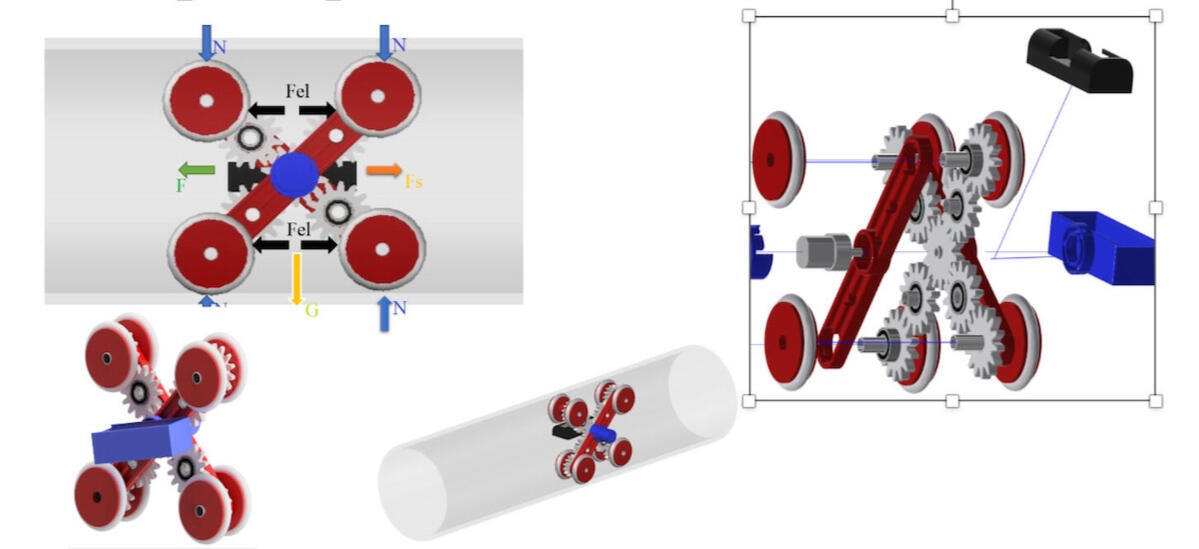
Modeling An In-Pipe Inspection Robot
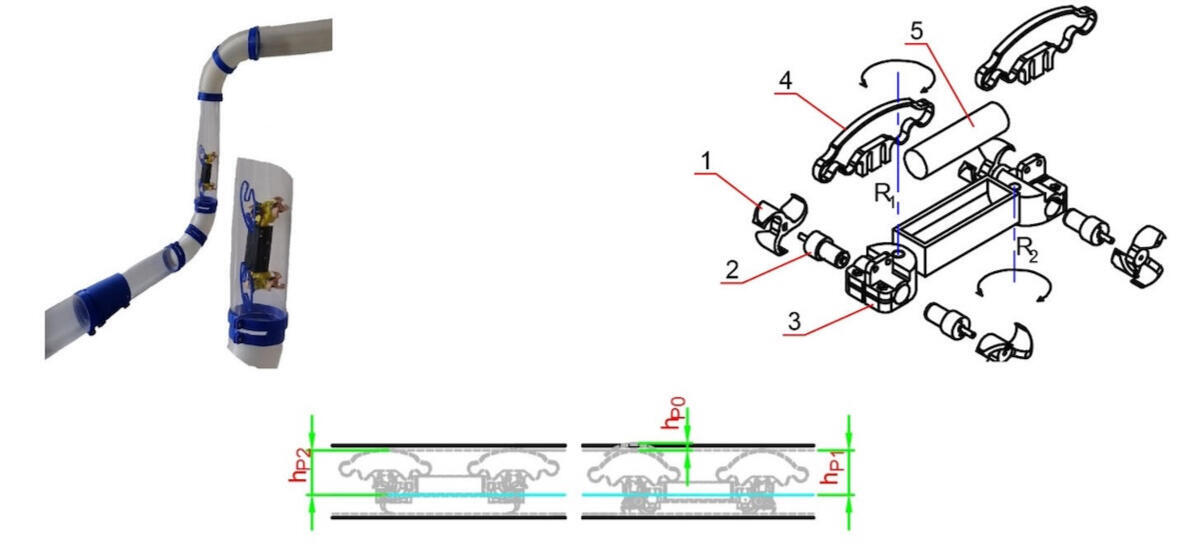
This paper presents the design and development of a novel mobile robot for in-pipe inspection, featuring six contact points with the pipe’s inner surface. The robot is constructed using 3D printing technology, enabling a lightweight and customizable design. It incorporates four independently driven modules and elastic elements to maintain stable contact with the pipe walls, ensuring effective locomotion across various pipe orientations and angles.A comprehensive analysis is conducted to determine the load distribution at the contact points, a critical factor for optimizing traction and maneuverability. The results of this analysis are graphically represented to illustrate the system’s performance. Additionally, experimental evaluations are performed to assess the robot’s ability to navigate complex routes within pipelines. The findings contribute to the advancement of autonomous in-pipe inspection technologies, improving efficiency and reliability in pipeline maintenance and monitoring.Dachkinov, P., Chavdarov, I., Pavlov, V., Modeling An In-Pipe Inspection Robot, Journal of Physics and Technology, ISSN 2535-0536 http://jpt.uni-plovdiv.bg/, 2017, Plovdiv University Press „Paisii Hilendarski"
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF 3D PRINTED AND ASSEMBLED ROTATIONAL UNITS. APPLICATIONS FOR MECHANISMS USED IN ROBOTICS
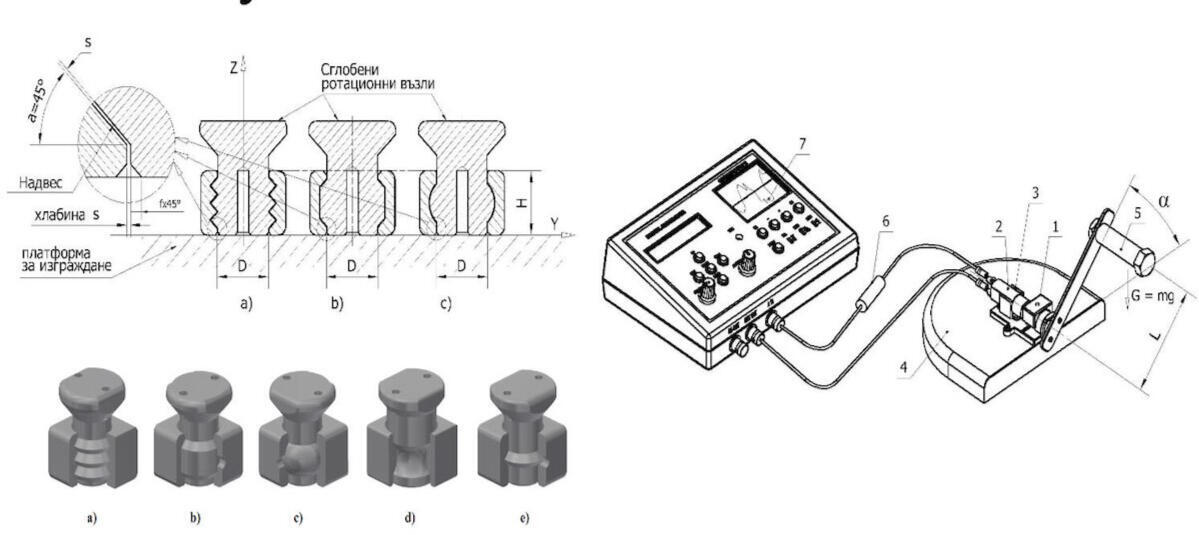
This paper explores the application of 3D printing as an additive manufacturing technology for the development of novel rotational assembly units. Various designs of assembled rotational mechanisms fabricated using 3D printing are presented. A detailed experimental analysis is conducted to evaluate the clearances within these constructions, providing insights into their impact on mechanical performance.The obtained results are further analyzed for optimization purposes, aiming to enhance the precision and functionality of the printed mechanisms. Additionally, potential applications of these optimized rotational units in robotic systems are discussed, demonstrating their relevance in advanced mechanical design. This study contributes to the refinement of 3D-printed mechanical assemblies, offering new possibilities for their implementation in robotics and automation.
Chavdarov, I., Dachkinov, P., Krastev, A., Trenev, V., Elenchev, G., Design and Analysis of Directly Assembled 3D Printed Rotational Unit. Applications in Robotics, (Published in Bulgarian) International Scientific Conference “Automation of the Discrete Manufacturing” XХVI, (2017). p-p. 412–416.
Design and Motion Capabilities of an Emotion-Expressive Robot EmoSan
Non-verbal communication plays a crucial role in human interaction, with head movements serving as key indicators of acceptance and affinity. This paper presents the development of an emotion-expressive robot designed to replicate human head motions, enhancing affective interaction between humans and robots. The robot’s movements are realized using a parallel mechanism based on the Gough-Stewart platform, allowing precise and dynamic head motion reproduction.
A comprehensive workspace analysis is conducted to assess the robot’s capability to mimic human head movements accurately. Additionally, the potential integration of brain signal processing, specifically electroencephalography (EEG), is explored as a means of coupling human emotions with robotic responses. This capability could enable novel applications, such as teaching children basic emotions through interactive play, fostering real-time emotional engagement. The findings of this study highlight the significance of head motion in non-verbal communication and demonstrate the potential of robotic systems in enhancing human-robot interaction through expressive movement.Dachkinov, P., Tanev, T., Lekova, A., Batbaatar, D., & Wagatsuma, H. (2018). Design and motion capabilities of an emotion-expressive robot EmoSan. Proceedings - 2018 Joint 10th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems and 19th International Symposium on Advanced Intelligent Systems, SCIS-ISIS 2018, 1320–1326. https://doi.org/10.1109/SCIS-ISIS.2018.00207
A Systematic Design and Analysis Method of Elastic 3D Printed Knee Supportive Orthotic Devices to Meet Individual Needs
This study focuses on the development of a novel orthotic device for the human knee joint by utilizing the compliant properties of flexible 3D-printed mechanisms. The primary objective is to address the need for customizable and cost-effective solutions, particularly in low-budget healthcare settings where affordable wearable options are currently limited. Additionally, this research aims to bridge the gap in rehabilitation devices by introducing an orthosis with adjustable flexibility, allowing for dynamic adaptation throughout the recovery process.Following a knee injury, patients often transition from rigid orthotic supports to soft fabric-based wearables, supplemented with low-impact rehabilitation exercises. However, the absence of an intermediate supportive device creates a critical challenge, particularly for athletes seeking a smoother and safer recovery process. The knee joint remains highly vulnerable during this transition, increasing the risk of re-injury. This study identifies a market gap for an orthotic device that offers adjustable elasticity, tailored to individual rehabilitation needs and lifestyle requirements. The proposed solution enhances patient recovery by providing a scalable and adaptable support system, ensuring a more effective rehabilitation experience.
Traditional rehabilitation devices lack the necessary flexibility and adjustability to fully accommodate the progressive nature of recovery. The study analyzes the distribution of moments and the compatibility of different support structures, demonstrating how parameters such as curvature radius and the number of flexures can be optimized for individualized rehabilitation. The proposed methodology supports resisted knee flexion and extension exercises, facilitating controlled improvements in range of motion (ROM) and quadriceps strength. As patients progress, they transition to more flexible devices until they achieve independent movement.Furthermore, an alternative categorization of the devices based on task completion rather than recovery time is introduced, providing a more personalized rehabilitation strategy. This adaptable framework enhances the effectiveness of ACL rehabilitation, reducing the risk of re-injury and improving patient confidence in performing functional movements independently
DETERMINING THE ELASTIC ROPERTIES OF FLEXIBLE 3D PRINTED BEAMS WITH VARIABLE INFILL DENSITIES AND PATTERNS
Flexible, non-linear 3D-printed materials are increasingly used in applications such as soft robotics, actuators, and medical devices. Their mechanical properties can be tailored by adjusting internal geometry and infill density, making them a focus of recent research. This study examines the effect of infill percentage and geometry on the mechanical behavior of 3D-printed flexible materials using a desktop FDM printer.
Beam samples with identical external geometry but varying infill densities (10% to 100% in 15% increments) and three infill patterns (rectangular, square, and honeycomb) are analyzed. An analytical approach, based on cellular solids theory, is used to determine in-plane stiffness properties. The results highlight significant stiffness variations despite the uniform external shape. A nonlinear finite element analysis (FEA) of a fully solid beam is also performed for comparison. The findings demonstrate how infill design can optimize the stiffness-to-weight ratio in flexible 3D-printed structures undergoing large deformations.
Bhattacharjee, A., Dachkinov, P., Wagatsuma, H., & Bhattacharya, B. (2022). 3D PRINTED BEAMS WITH VARIABLE INFILL DENSITIES. 1–12.
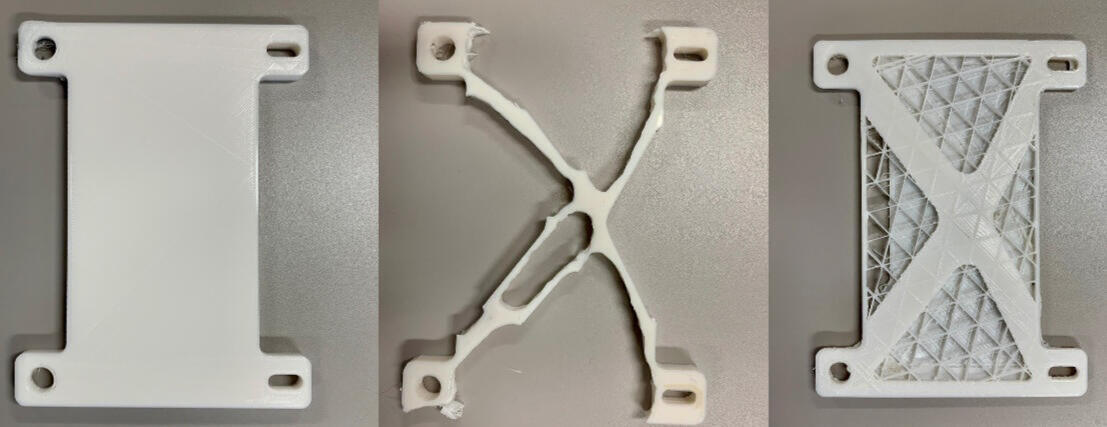
Topology Optimisation

Cheetah Robot
Compliant Mechanisms
The design of 3D-printed cross-spring compliant joints is gaining attention for its versatility across various applications, particularly in precision engineering and robotics. These joints leverage flexible materials with different mechanical properties to enable motion through elastic deformation, offering a frictionless and wear-free alternative to traditional pivots.
This study presents a modified cross-spring pivot design optimized for in-plane motion. A nonlinear finite element analysis (FEA) is conducted to evaluate its mechanical behavior under various loading conditions. With the growing capabilities of 3D printing in fabricating complex geometries, compliant mechanisms are poised to revolutionize the design of high-precision actuators and robotic manipulators by enhancing performance, durability, and efficiency.
Dachkinov, P., Bhattacharjee, A., Bhattacharya, B., & Wagatsuma, H. (2022). A Three-Dimensional Design of the Multi-material Joint System to Realize a Structural Spring-Damper Compliant Mechanism with Versatility in Engineering Fields. Proceedings of International Conference on Artificial Life and Robotics, 193–200. https://doi.org/10.5954/icarob.2022.gs3-1
Mechanisms





















